WebAssembly Image Processing: A New Paradigm for Ultimate Performance and Absolute Privacy
2025-09-20
1. Introduction to AI and Traditional Image Processing
The rise of AIGC (AI-Generated Content), particularly diffusion model-based text-to-image technology, has completely changed how we create images. The process typically involves complex computations on powerful GPU clusters in the cloud, with the final images being transferred over the network to the user or temporarily stored in the cloud for viewing and display.
Meanwhile, traditional image processing SaaS applications (like online format converters or compression tools) also predominantly use a cloud-based approach. This workflow inevitably involves multiple steps: the user uploads the original image, the file is stored and computed on the cloud, and the user then downloads the result. This entire chain not only increases server bandwidth and computation costs but also exposes the user's image data to multiple potential privacy risks.
2. The Problem with Traditional Image Processing: The "Last Mile" of Privacy
To protect data security, the entire chain of traditional image processing (upload, storage, download) typically uses TLS/SSL encrypted transmission. This significantly enhances the security of data in transit, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
However, an unavoidable "last mile" problem exists: the image must be decrypted into its raw data form when it reaches the cloud server for processing. Regardless of how robust the service provider's privacy policy is, from a technical standpoint, the moment your image resides in the server's memory, it is unencrypted. This might be acceptable for casual photos. But if a user needs to process highly sensitive data—such as ID photos with personal information, confidential business designs, private family photos, or even medical images—any form of upload introduces an unacceptable risk of a privacy breach.
WebAssembly local computing fundamentally solves this problem. When all image processing occurs within the user's local browser, the image file never leaves the user's computer. It is not transferred over any network, so there is no possibility of it being intercepted by a third party or temporarily stored on a server. This provides an unprecedented level of data privacy, allowing users to confidently process any extremely private images, knowing they are the only ones who will ever see the files.
3. Performance Concerns with Local Computing
Many might worry, "How can the computing power in a browser compare to professional servers in the cloud?" For tasks like AIGC that require massive computational power, this is true. But for the vast majority of everyday image processing tasks (compression, resizing, cropping, format conversion, etc.), WebAssembly demonstrates astonishing performance.
WebAssembly is a low-level binary format designed for the browser, allowing us to write code in high-performance languages like Rust and run it at near-native speed. We conducted a test: on a 5-year-old MacBook Pro, resizing a 1024*768 image using the WASM-based ats-studio took only ~100 milliseconds.
The reason it's so fast is that it completely eliminates network latency. With traditional cloud processing, 95% of the user's time is spent waiting for uploads and downloads; the actual computation time might be very short. Local WASM processing, however, dedicates all its time to the core computation, providing users with nearly instantaneous feedback.
4. Resizing an Image with ats-studio Image
Experiencing the ultimate speed and security of local WASM processing is simple.
4.1 Log in to aitoolsets.net
Visit our website and log in to your account.
click right-top
Sign In.
Select a Google account to login.
4.2 Enter the Studio
After logging in, navigate to the Image Studio from the navigation bar.
4.3 Select the Resize Tool
In the tool menu on the left, expand "Transform" and select "Resize".
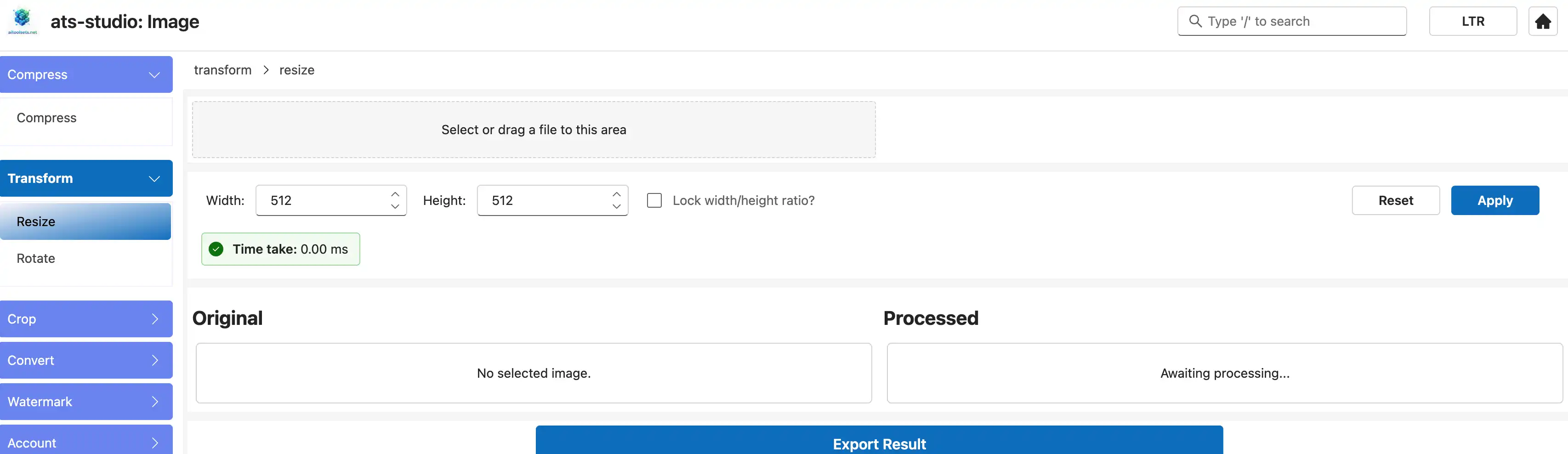
4.4 Load an Image
Drag and drop or select a input of any local image into the main content area. The image will appear instantly. Note that it has not been uploaded.
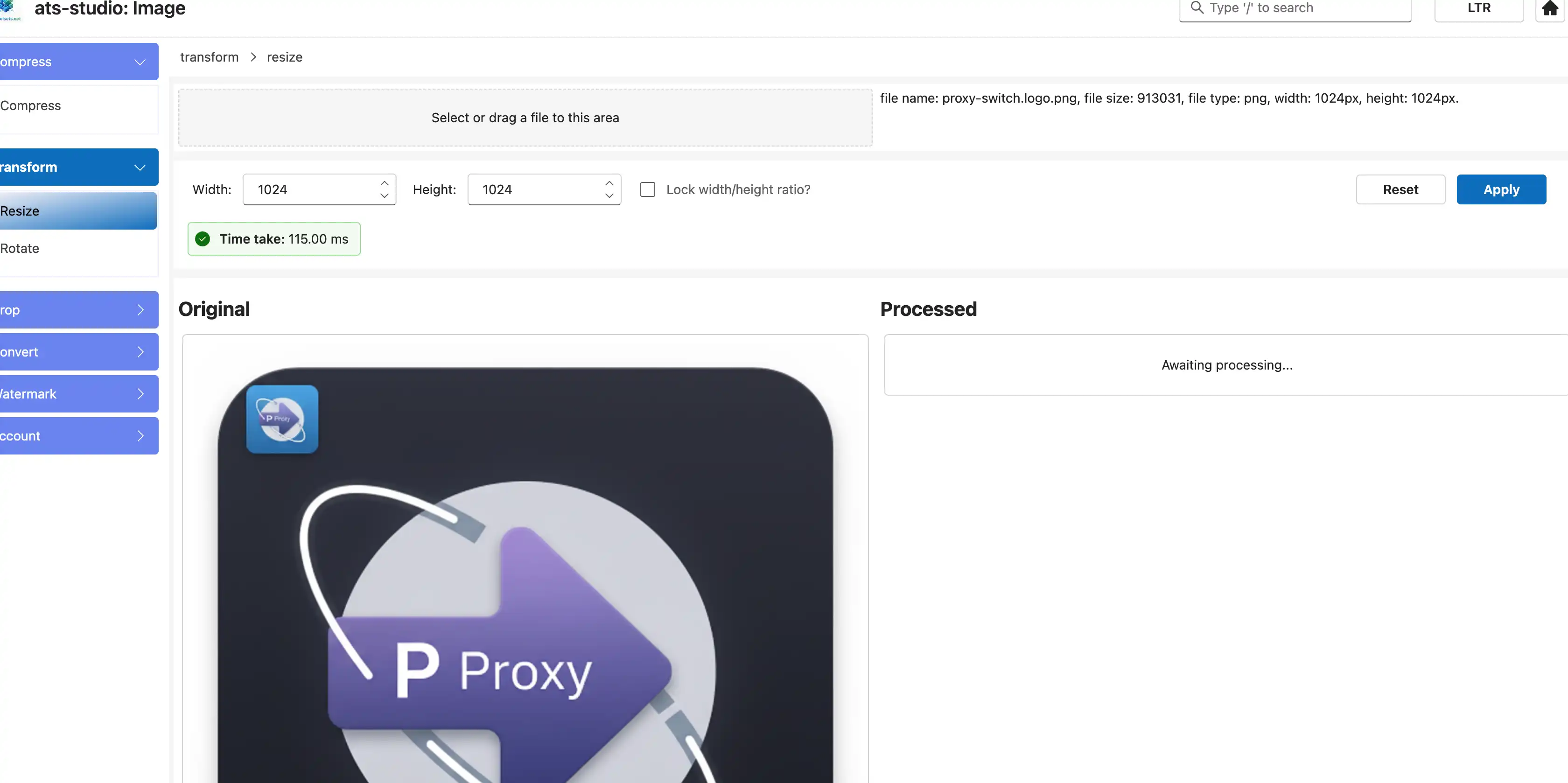
4.5 Set Parameters
In the toolbar in the middle, enter your desired width and height.
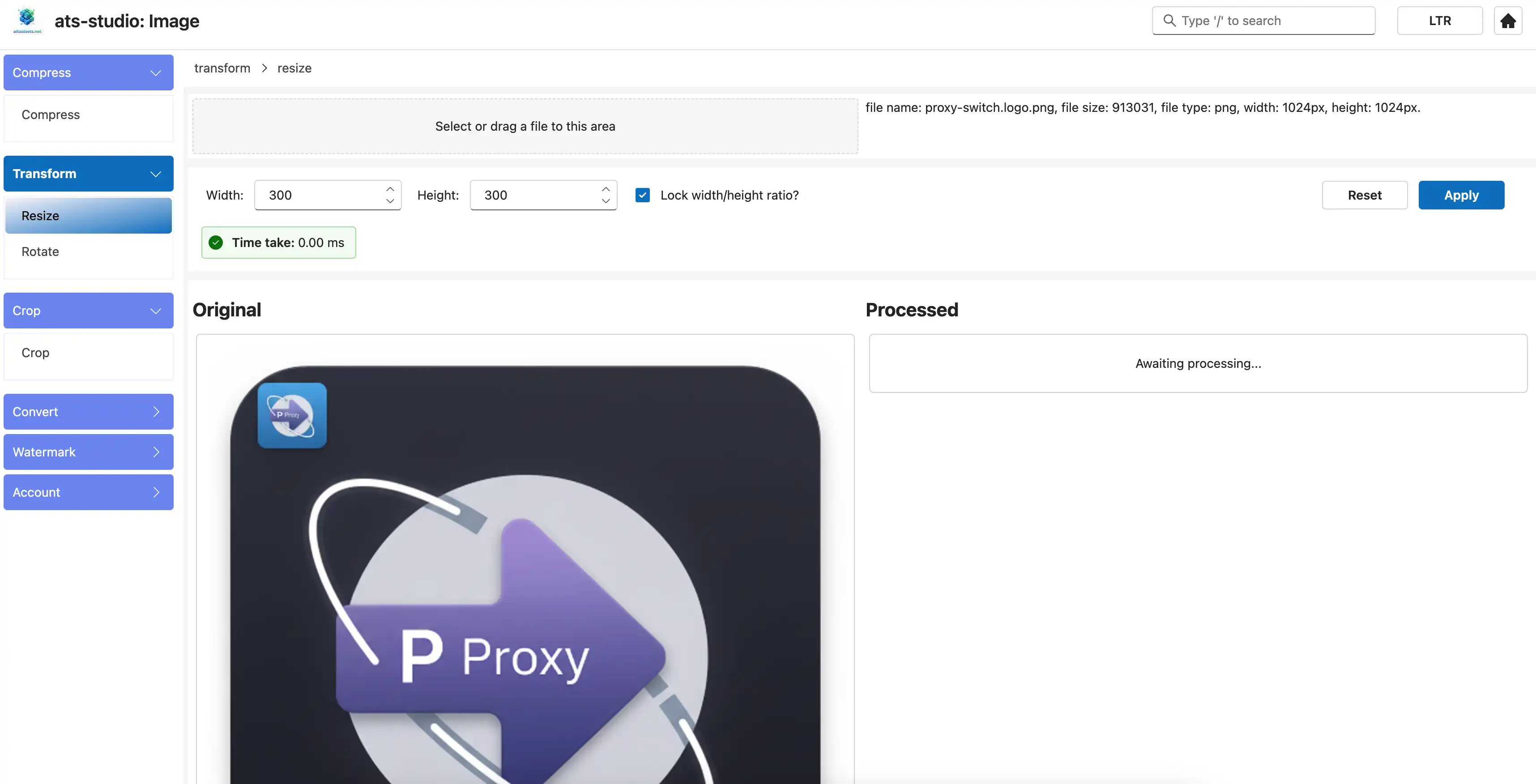
4.6 Apply
Click the "Apply" button. You'll notice the preview on the right updates almost instantly.
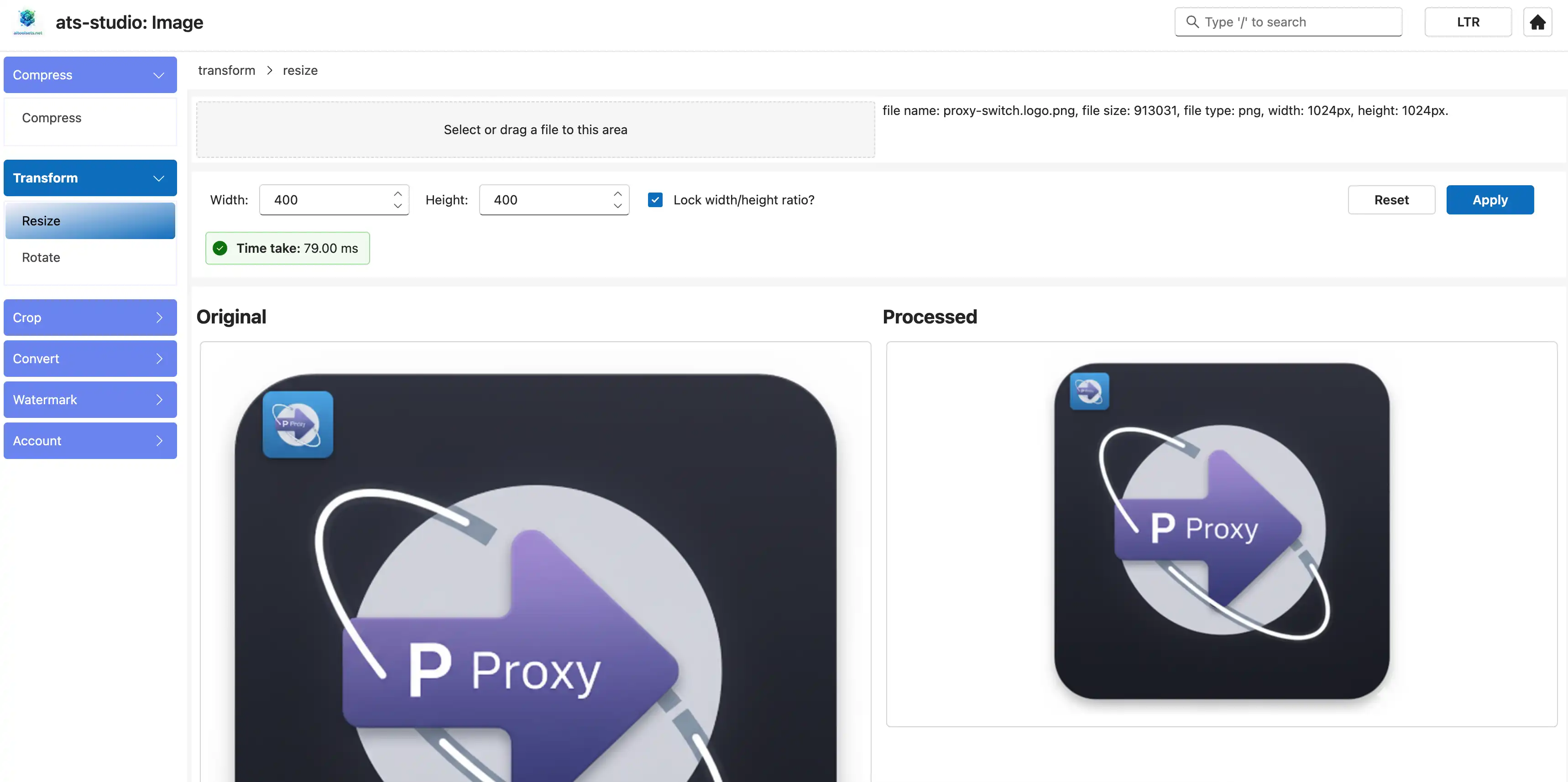
4.7 Observe the Time
The entire process, from clicking "Apply" to seeing the result, has almost no perceivable delay, even for larger images.
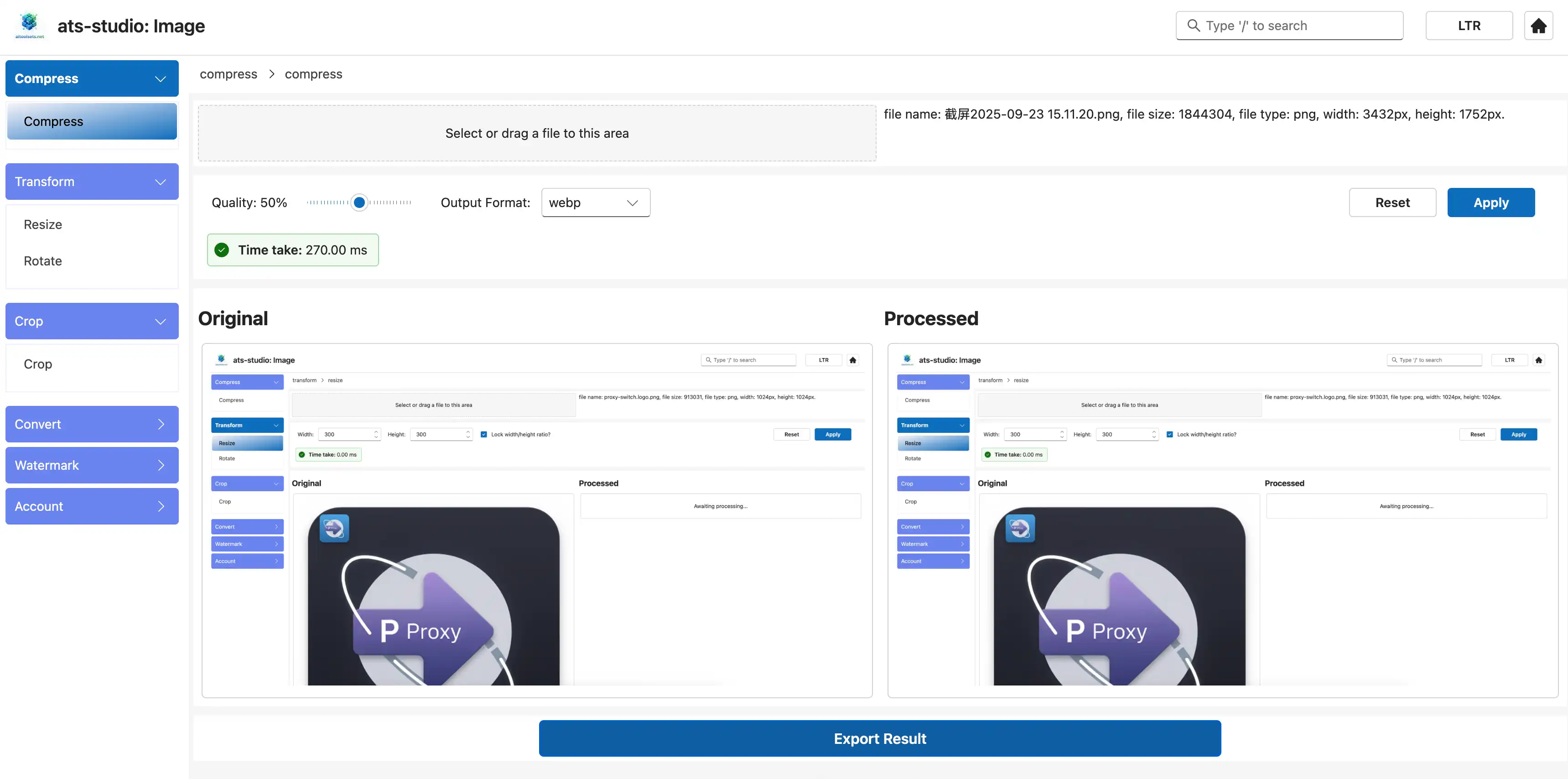
4.8 Crop and Compress an image
Screen show for crop:
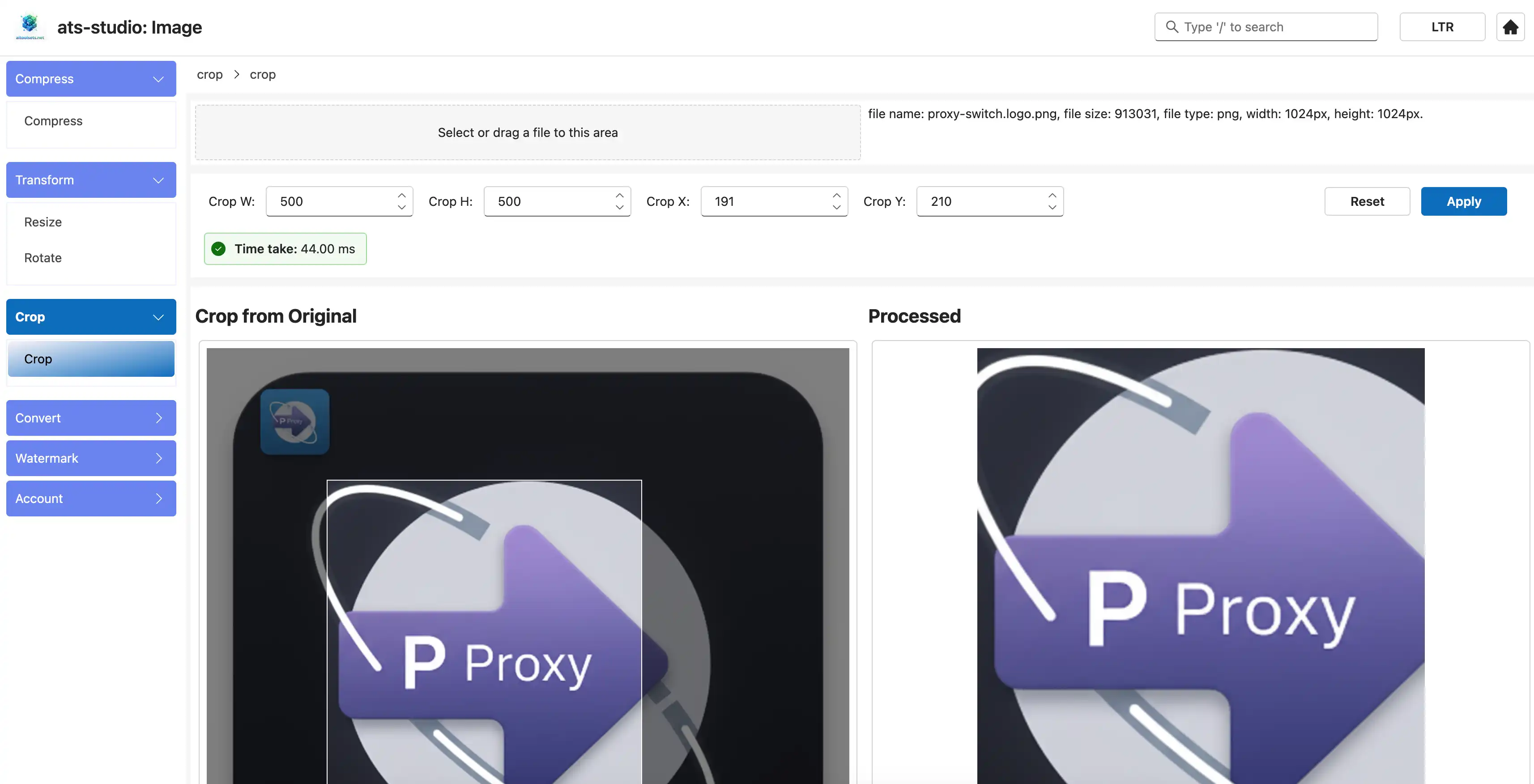
Screen show for compress:
5. Conclusion
WebAssembly is ushering in a new era for web applications. It brings the high-performance computing capabilities, previously exclusive to native desktop applications, safely into the browser. By bringing computation back to the local device, we not only provide users with greater speed but, more importantly, empower them with true data sovereignty and absolute privacy. Image processing is just the beginning; the infinite potential of WASM is waiting for you to explore.